6 Tips on Diabetes Management
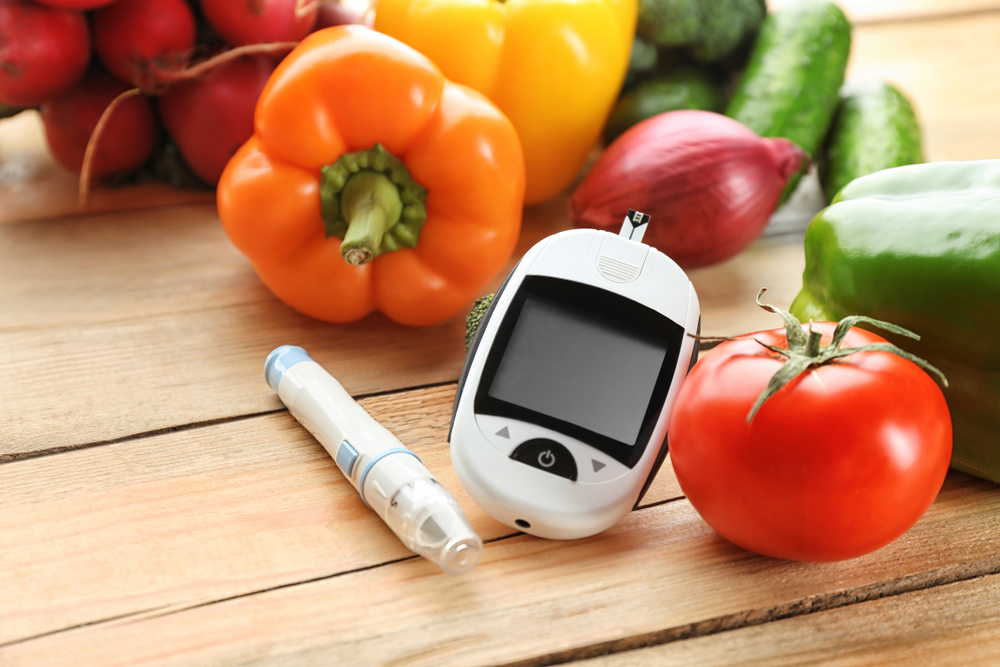
Diabetes is a non-communicable disease, a metabolic condition common among adults and youth. Diabetes results in high blood sugar levels (blood glucose). It occurs due to the failure of the pancreas to produce sufficient or no insulin, a hormone that stores glucose in your body as a source of energy. When left untreated, it can lead to various health problems such as; stroke or kidney problems and can be detrimental to your overall health.
This article shows you what diabetes is all about, the importance of using diet to address this serious health concern and manage the body’s sugar levels for overall health and well-being.
Types of Diabetes.
- Type 1 diabetes: type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes (mainly diagnosed in young people and children), is a condition where the immune system destroys the cells that generate the insulin hormone. Since there is damage to cells, glucose cannot move to the cells. As a result, a glucose build-up is created, causing high blood sugar.
- Type 2 diabetes: is the most common variety and is diagnosed in adults prone to insulin resistance. The pancreas may generate ample insulin and deliver glucose into the cells. Yet, it may eventually fail to continue the process, resulting in Type 2 diabetes.
- Prediabetes: a condition when the blood sugar level is higher than the average level but not enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. However, it ultimately leads to Type 2 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: a diabetic condition found in pregnant women, is among the other common diabetic conditions.
While the exact cause for diabetes is not identified, health professionals believe that genetics and environmental factors often trigger the disease. On the other hand, diabetes is not evidently curable. However, it can be treated and prevented effectively with consistent and proper medical treatment when diagnosed on the spot.
Common Diabetes symptoms
Most of the times, a potential diabetic patient shows symptoms such as;
- Increased hunger and thirst
- Drastic weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Slow-healing wounds
- Blurry vision.
It is essential to seek medical advice and get yourself a clinically proven diabetes management plan in such a case.
Diabetes and Diet
In addition to the medical treatment, you can adhere to a curated plan to curb the disease and manage your elevated blood sugar levels. Most importantly, blood sugar control should be the primary concern in an attempt to manage diabetes including the following:
- It is crucial for people living with diabetes to reduce their daily sugar intake, especially any added (artificial) sugars found in sweetened drinks (including soft drinks), sweets, and ready-made meals. Most of the meals and fruits we consume daily naturally contain sugar; they do suffice the required amount of sugar for the body.
- Incorporating anything that consists of any added sugar is not advised to regulate high blood sugar levels. For example, you can include fruits in a diet instead of substituting the whole fruits with smoothies with added sugar.
- Also, obesity/ gaining extra weight is a high-risk factor for developing Type 2 diabetes. Weight control and an effective diet plan can tremendously help you manage the disease itself.
- To manage this condition, a well-balanced, healthy diet, excluding any added sugar, high fat and sweetened dairy products, high calories- along with simple changes to your eating patterns, is vital to maintain healthy sugar levels of your body.
- Incorporate food, fruits, veggies, and dairy products, whole grains that are low on sugar, carbs, and fat (oats, chia seeds, Greek yogurt, citric fruits, and spinach), shows a positive impact on weight and glucose levels.
(a high-fat, low-carb diet) plans are highly recommended for diabetic patients (especially Type 2). It is equally important to check your carb intake as high levels of carbohydrates can affect your insulin.
Following a workout routine consistently is fundamental to regulating blood glucose, body weight and improving your overall health. From cardio exercises to walking and jogging, exercise is one of the optimum treatments for diabetes. It is advised that people living with diabetes should aim to engage in physical activity for at least 150 minutes per week. Yoga exercises are also recommended as an effective method of exercise for diabetes control.
While diet control and exercise are the keys to managing diabetes, you need to take medically approved combinations of several drugs simultaneously to prevent the disease from getting out of control. With simple yet conscious lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating habits, weight loss, engaging in physical activities, stress management, and reducing alcohol consumption, you can undoubtedly treat the disease.




Comments (0)