5 Health Benefits of Banana
Banana is a tropical and edible fruit from the family of plants called Musa that is primary to Southeast Asia and grown in many warmer regions of the world. Banana is one of the most important and common food crops in the world. This edible and highly nutritious fruit contains fiber, potassium, vitamins, antioxidants, and phytonutrients essential for your health and wellbeing. Banana is in different colors from green to yellow, and red.
Banana is rich in carbs, occurring as starch in unripe bananas and as sugar in ripe ones. The carbs make-up of banana changes rapidly during ripening, during this phase, starch is converted into sugars and ends up being less than 1% when it finally ripened. The most common sugars in ripe bananas are sucrose, fructose, and glucose; the total amount of sugar in a ripe banana can be more than 16% of its fresh weight.
Nutritional Composition of Banana
The nutritional composition of banana can vary slightly depending on its size, but the values provided below are based on a medium-sized banana, approximately 118 grams.
- Calories: A medium-sized banana contains about 105 calories, making it a relatively low-calorie food option.
- Carbohydrates: Bananas are primarily composed of carbohydrates. A medium-sized banana contains approximately 27 grams of carbohydrates, including sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose. These natural sugars provide a quick and sustained energy boost.
- Dietary Fiber: Banana is a good source of dietary fiber. A medium-sized banana provides about 3 grams of fiber, which aids in digestion, promotes satiety, and supports a healthy digestive system.
- Protein: While banana is not a significant source of protein, they still contain a small amount. A medium-sized banana typically contains about 1 gram of protein.
- Vitamin C: Banana is a decent source of vitamin C, an essential antioxidant that supports the immune system, aids in collagen production, and acts as a powerful antioxidant. A medium-sized banana can provide around 10% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C.
- Vitamin B6: Banana is rich in vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine. Vitamin B6 plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, brain development, and the production of red blood cells. A medium-sized banana contains approximately 20% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin B6.
- Potassium: One of the standout nutritional aspects of banana is its high potassium content. Potassium is an essential mineral that helps maintain proper heart function, regulates blood pressure, and promotes muscle and nerve function. A medium-sized banana provides about 400 milligrams of potassium, which is approximately 9% of the recommended daily intake.
- Magnesium: Banana is also a good source of magnesium, an important mineral involved in various bodily processes such as energy production, nerve function, and muscle contraction. A medium-sized banana contains around 8% of the recommended daily intake of magnesium.
Other Nutrients: Banana contains small amounts of other essential nutrients, including vitamin A, vitamin E, folate, niacin, riboflavin, and calcium. These nutrients contribute to overall health and well-being.
It's important to note that the nutritional composition of banana can slightly vary based on its ripeness. As banana ripens, their starch content converts into sugars, resulting in a sweeter taste and higher sugar content.
The Amazing Benefits of Banana
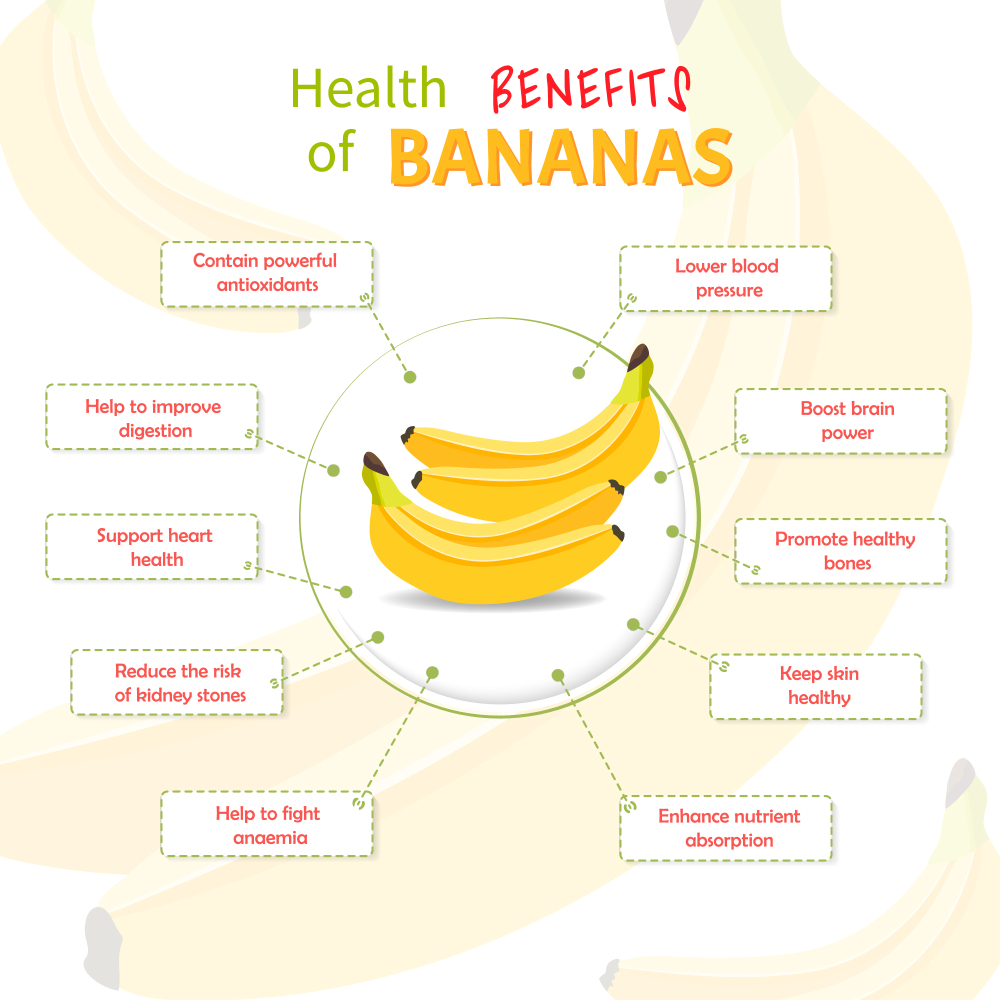
Good for the Heart
Banana is rich in minerals such as potassium; potassium improves heart health and blood pressure. A medium banana has about 0.4g of potassium, and various studies suggest that daily intake between 1.3-1.5 grams of potassium can lower the risk of heart disease up to 26%. Also, a high amount of antioxidants such as flavonoids can cause a substantial decrease in cardiac disease risk.
Source of Energy
Feeling low on energy? Grab a banana! The yellow powerhouse is a fantastic natural energy source. The calorie in banana serves as a natural energy booster when you need to exercise or feel weak. A medium banana has about 105 calories, and two medium bananas can provide the calories required for 45 -90 minutes of exercise. It is a better and healthier source of energy instead of cakes, and energy drinks.
Additionally, banana is rich in carbohydrates, making them an ideal pre- or post-workout snack for replenishing glycogen stores and aiding muscle recovery.
Also, Read:
Healthy Gut
Banana is well-known for its digestive benefits. Unripe, green banana contains different types of fiber which are the pectin and resistant start. These dietary fibers serve as prebiotic nutrients, encouraging the growth of healthy gut bacteria. These fibers are fermented by the healthy bacteria in the gut and undergo a reaction by converting to butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that promotes a healthy gut.
Lowers Blood Sugar Levels
Banana especially unripe banana is believed to be good for people with type 2 diabetes. However, due to high starch and sugar in banana, there have been different opinions about how beneficial banana is in reducing and stabilizing blood sugar level. Banana has a low glycemic index, portion control or moderate intake of this delicious fruit should not increase your blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, you are encouraged to avoid eating lots of fully ripened bananas and watch your blood sugar levels closely after eating high sugar and carbs food.
Boost Memory and Mood
Banana not only nourishes the body but also have a positive impact on mood and mental well-being. Banana is high in phytonutrients and amino acids such as tryptophan. They play a role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, and it may preserve memory by improving your ability to learn. Consuming banana can help elevate serotonin levels in the brain, promoting a sense of relaxation and happiness.
Versatile Culinary Ingredient
Beyond their impressive nutritional profile, banana is incredibly versatile in the culinary world. It can be enjoyed in numerous ways, such as eating it raw, sliced over cereal, blended into smoothies, mashed or baked into bread, cookies or muffins, or even frozen for a refreshing treat. This versatility adds to their appeal and makes incorporating bananas into your diet an enjoyable and delicious experience.
Conclusion
Banana is much more than a tasty snack. It is a tropical nutritional powerhouse, rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. It provides a range of benefits from promoting heart health to supporting digestion, aid weight loss and offering a natural energy boost. Incorporating bananas into your daily diet is a smart choice for anyone looking to enhance their overall well-being. So, the next time you reach for a snack, consider reaching for a banana and experience the multitude of health advantages it has to offer.
BY: By Gift Chinecherem Ujuaku




Comments (0)